Contraception
Contraception, also known as birth control or family planning, refers to the methods and techniques used to prevent pregnancy. There are various contraceptive methods available, offering individuals and couples the ability to make informed choices about when and if they want to have children. Here are some common methods of contraception:
Barrier Methods:
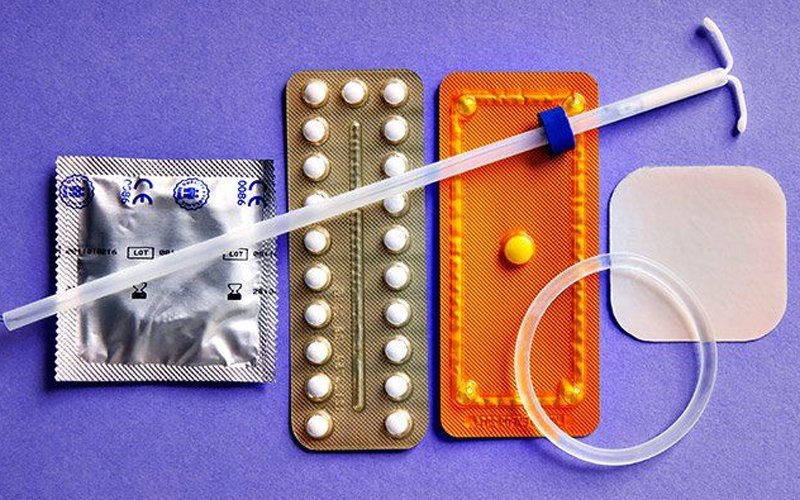
- Condoms: Male and female condoms are physical barriers that prevent sperm from reaching the egg. They also provide protection against sexually transmitted infections (STIs).
- Diaphragm and Cervical Cap: These are barrier devices that are inserted into the vagina to cover the cervix, preventing sperm from entering the uterus.
Hormonal Methods:
- Birth Control Pills: Oral contraceptives contain hormones (estrogen and/or progestin) to prevent ovulation and alter the cervical mucus, making it more difficult for sperm to reach the egg.
- Birth Control Patch: This is a transdermal patch that releases hormones through the skin to prevent ovulation.
- Birth Control Shot (Depo-Provera): This injectable contraceptive contains progestin and provides protection against pregnancy for about three months.
Long-Acting Reversible Contraception (LARC):
- Intrauterine Devices (IUDs): Small, T-shaped devices inserted into the uterus. They can be hormonal or non-hormonal and provide protection for several years.
- Implants: Small rods inserted under the skin that release hormones to prevent ovulation. Implants provide protection for several years.
Emergency Contraception:
- Emergency Contraceptive Pills (Morning-After Pill): These pills can be taken after unprotected sex to reduce the risk of pregnancy. They are most effective when taken as soon as possible after intercourse.
Sterilization:
- Tubal Ligation (for women): A surgical procedure that involves blocking or sealing the fallopian tubes, preventing the egg from reaching the uterus.
- Vasectomy (for men): A surgical procedure that involves cutting or sealing the tubes that carry sperm.
Fertility Awareness Methods:
- Natural Family Planning: Involves tracking menstrual cycles, monitoring basal body temperature, and observing cervical mucus changes to identify fertile days and avoid unprotected intercourse during those times.
Withdrawal (Pull-Out) Method:
- Withdrawal: Involves the man withdrawing his penis from the vagina before ejaculation. This method is less effective than many other forms of contraception.